glucoamylase enzyme
Release date:
2025-07-11
Declared Enzyme: | Glucoamylase |
Systematic Name: | EC 3.2.1.3, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan glucohydrolase |
Appearance: | Yellow brown brown liquid |
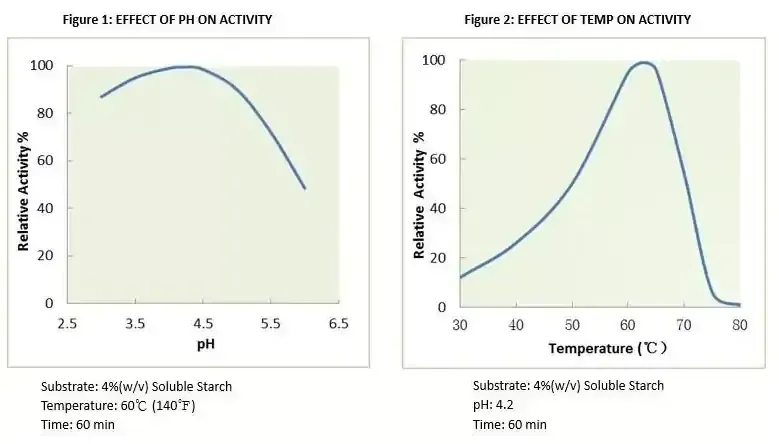
Activity: | 400,000 U/ml (minimum) |
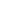
Product pH: | 3.0 to 5.0 |
Specific gravity: | ≤1.20 g/ml |
- Standard packaging is 25kg, 30kg food grade plastic drums or 1125kg IBC totes. Customized packaging is available upon request.
- Typical shelf-life is eighteen months if it is stored below25°Cin its original packaging, sealed and unopened, protected from direct sunlight.
- Prolonged storage and/or adverse conditions such as higher temperatures may lead to a higher dosage requirement, therefore should be avoided.

Glucoamylase enzyme is a highly efficient and versatile biocatalyst widely used in various industries for its ability to break down complex carbohydrates into simple sugars. One of the key advantages of glucoamylase is its ability to work under a broad range of conditions, including moderate temperatures and slightly acidic to neutral pH levels, making it suitable for diverse processing environments.
In the food and beverage industry, glucoamylase plays a vital role in the production of sweeteners, syrups, and fermented products. It is extensively used in the saccharification step of starch-based processes, where it efficiently converts dextrins and oligosaccharides into glucose, enhancing yield and reducing processing time. The enzyme’s high specificity ensures minimal byproduct formation, resulting in purer and more consistent end products. Additionally, its application in brewing and alcohol production improves fermentation efficiency by maximizing sugar availability for yeast, leading to higher alcohol yields and better-quality beverages.
Another significant application of glucoamylase is in the biofuel industry, where it aids in the conversion of starch-rich feedstocks, such as corn and cassava, into fermentable sugars for ethanol production. The enzyme’s robustness and effectiveness contribute to cost-efficient and sustainable biofuel manufacturing. Beyond industrial uses, glucoamylase is also employed in research and diagnostics, particularly in enzymatic assays and biochemical studies involving carbohydrate metabolism.
The benefits of using glucoamylase include its high catalytic efficiency, stability under processing conditions, and compatibility with other enzymes, allowing for synergistic effects in multi-enzyme systems. Its use leads to reduced energy consumption, lower production costs, and improved product quality, making it a preferred choice for manufacturers worldwide. Whether in large-scale industrial processes or specialized applications, glucoamylase enzyme stands out as a reliable and essential tool for starch hydrolysis and sugar production.